Eu2O3/carbon-nanospheres for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B dye
Release time:2025-03-04
Hits:
Impact Factor4.2
DOI number:10.1016/j.mssp.2025.109422
Journal:Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing
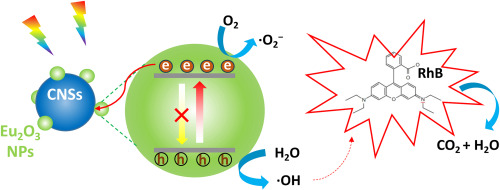
Abstract:The demand for water pollution control accelerated the development of environment-friendly technologies, e.g., photocatalysis, for resolving the pollution issue efficiently. Wide bandgap rare earth oxide semiconductors are potential photocatalysts with low toxicity for the environment, but the luminescence of rare earth ions and narrow light absorption band restrict their photocatalytic degradation efficiency. In this study, we synthesized a composite structure consisting of Eu2O3 nanoparticles (NPs) and carbon-nanospheres (CNSs) by annealing both monomers in argon atmosphere together. The photocatalytic degradation performance of the composites with different mass ratios were investigated by utilizing rhodamine B (RhB) dye as the target organic pollutant. The results show that the combination with CNSs significantly improved the photocatalytic performance of Eu2O3, and the composite's highest removal efficiency reached up to 55 % within 60 min, which is competitive to those for other rare earth oxides. The improved photocatalytic degradation capacity for the composite structure was attributed to the luminescence suppression of Eu3+ and the increased visible-light absorption by CNSs. Our research sheds light on the possible routes for enhancing the photocatalytic degradation capability of rare earth oxides in the environment pollution abatement.
Indexed by:Journal paper
Document Type:J
Volume:192
Issue:0
Page Number:109422
Translation or Not:no
Date of Publication:2025-03-01
Included Journals:SCI
First Author:Jialong Ma
First Author:Yishuai Jing
Correspondence Author:Jiaming Song
All the Authors:Yuting Li
All the Authors:Shanbo Cui
All the Authors:Xin Zhao